Improving Nasal Electrolaryngeal Speech Using Voice Conversion
Abstract
Electrolaryngeal (EL) speech produced by laryngectomees using an electrolarynx has low intelligibility due to insufficient excitation signals for speech production and fixed pitch. Although recent EL speech voice conversion (ELVC) research has made good progress, the research has mainly focused on cervical EL (CEL) speech. This study experiments on ELVC of speech produced by a novel nasal EL (NEL) device. Specifically, we evaluate the impact of using Mel-spectrogram and WavLM features as inputs to the ELVC system. We also propose a data augmentation method using text-to-speech (TTS) and exemplar-based VC. We find that while WavLM features have a significant effect on ELVC of CEL speech, the model using Mel-spectrogram performs better in both subjective and objective evaluations of ELVC of NEL speech due to the unique acoustic properties of NEL speech. In addition, NEL speech synthesized using Mel-spectrogram is closer to real NEL speech than NEL speech synthesized using WavLM features.
Architecture and Experimental Settings
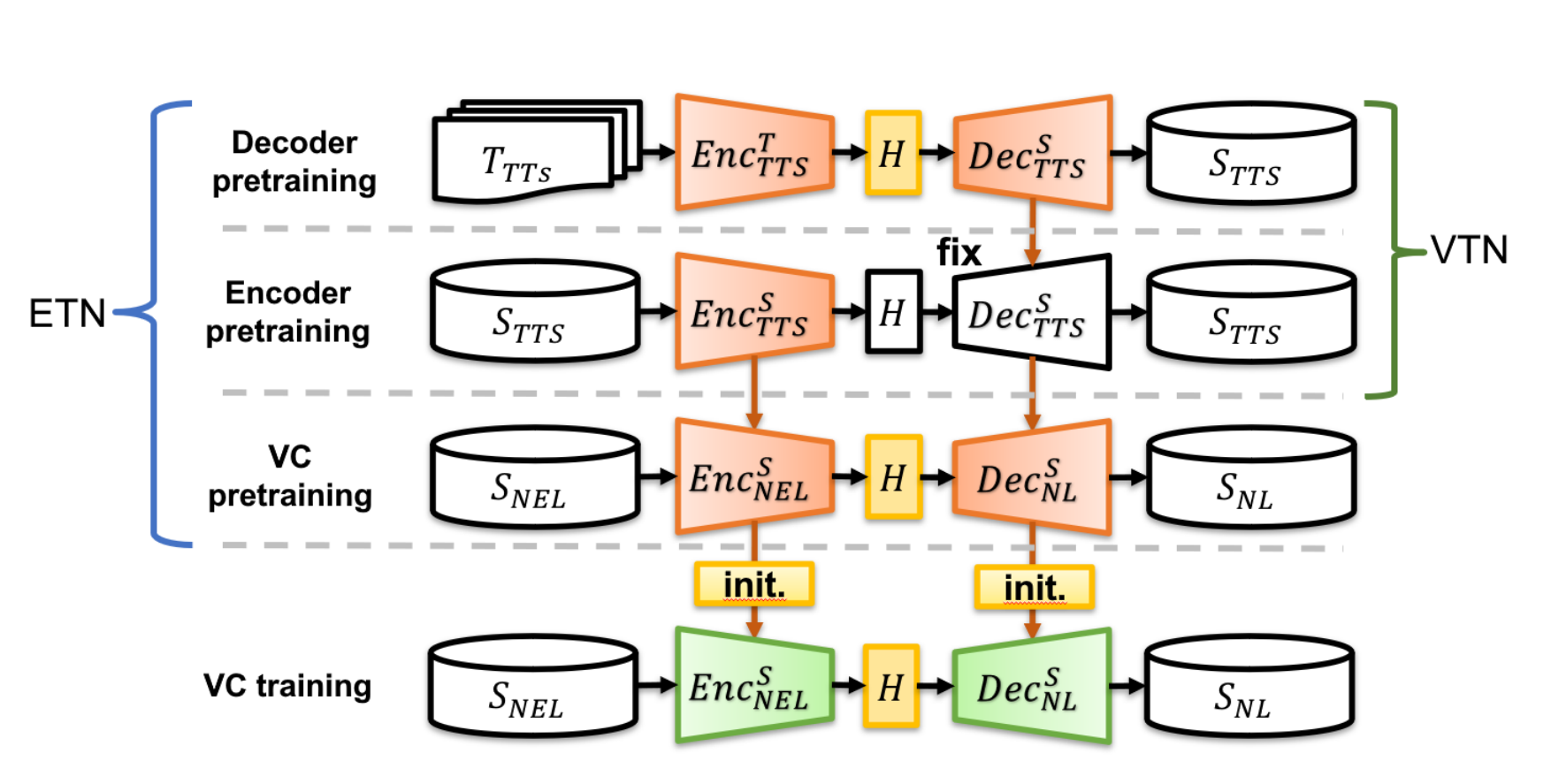
- Fig. 1. The training process of VTN-VC and ETN-VC models.
-
VTN-VC: Two pretraining stages with a large-scale NL corpus; VC training stage with the EL dataset.
-
ETN-VC: Two pretraining stages with a large-scale NL corpus; VC pretraining stage with the sEL and EL corpora; VC training stage was further fine-tuned on the EL dataset.
EL dataset
- CEL-NL: 320 utterances of parallel corpus
- NEL-NL: 320 utterances of parallel corpus
- All utterances were recorded by the same speaker.
sEL dataset
- TWnews: 10,000 generated utterances as augmented parallel corpus
- GPTgen: 10,000 generated utterances as augmented parallel corpus
The sNL/sEL data were generated based on the above EL dataset.
Evaluation Metric
Intelligibility related:
- MCD: Mel-cepstrum distortion ↓
- CER: character error rate of Whisper ASR ↓
- SER: syllable error rate of ASR system ↓
- A/B Test
- MOSA-Net+ ↑
Speech Quality related:
- UTMOS ↑
- UTMOSv2 ↑
- MOSA-Net+ ↑
F0 (Pitch) related:
- F0 RMSE: F0 root mean square error ↑
- F0 CORR: F0 correlation coefficients ↓
Duration related:
- DDUR: average absolute duration difference between the converted and target utterances ↓
Semantic Consistency related:
- SpeechBertScore ↑
Experimental Results
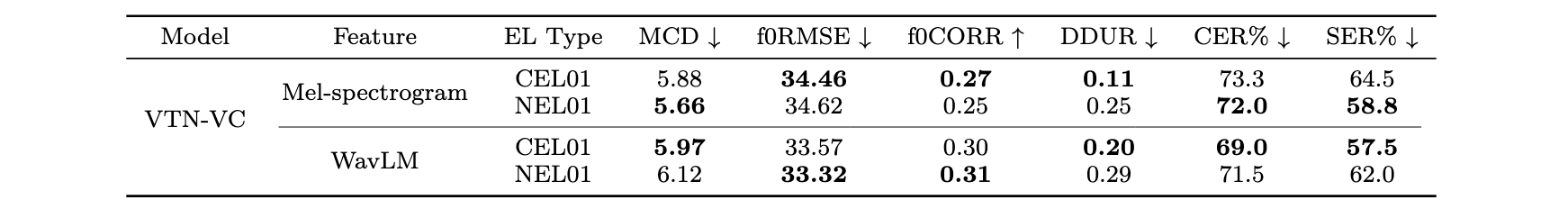
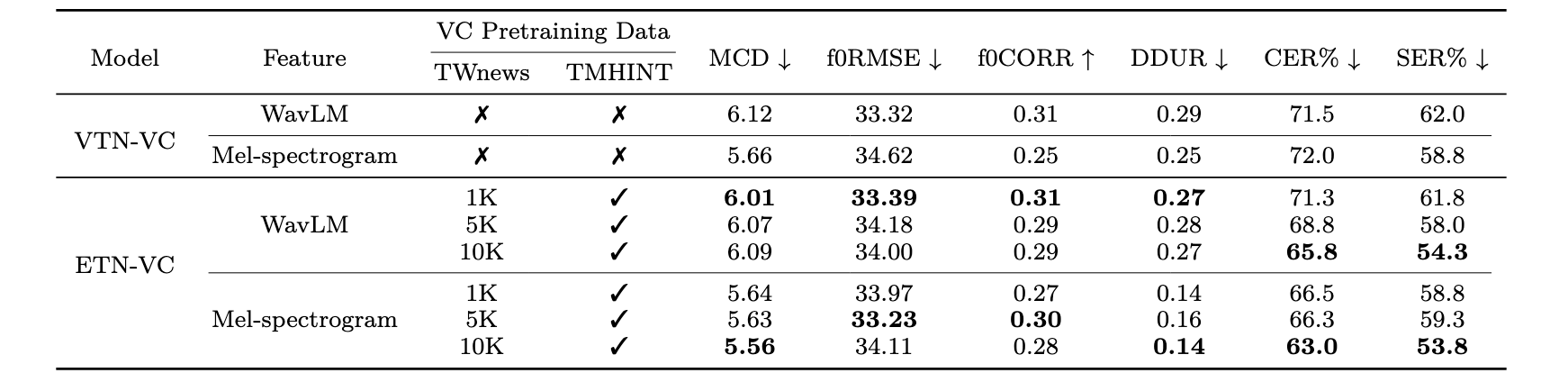
We evaluate the performance of VTN-VC on both CEL-to-NL and NEL-to-NL conversion, highlighting how the acoustic differences between CEL and NEL speech influence model behavior. To further analyze the characteristics of sNEL speech, we synthesized it using Mel-spectrogram and WavLM features, and examined their effectiveness in reconstructing the key resonant regions of NEL speech. We also compare VTN-VC and ETN-VC on the NEL-to-NL task to assess the impact of different training strategies and feature representations.
The baseline CER and SER for unprocessed NEL speech are 90.8% and 89.5%, respectively, while the zero-shot Seed-VC model achieves 92.3% and 84.8%. The following presents the results of NEL speech converted by the VTN-VC and ETN-VC models.
-
Table. I. Objective evaluation results of VTN-VC models using different features on CEL-to-NL and NEL-to-NL conversion tasks. ↑ means the higher the better, while ↓ means the lower the better.
-
Table. II. Performance comparison of the VTN-VC model and the ETN-VC model with different levels of data augmentation.
-
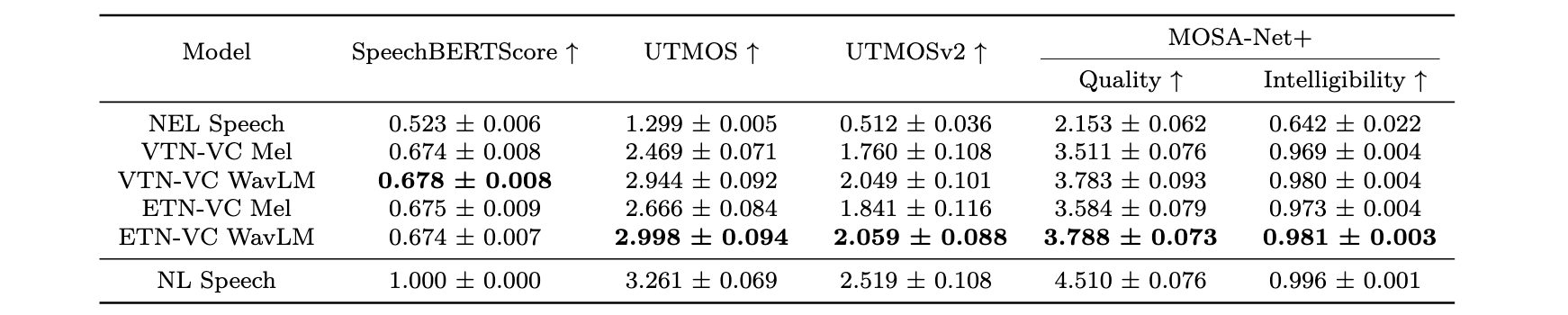
Table. III. SpeechBERTScore, UTMOS, UTMOSv2, and MOSA-Net+ scores for NEL, NL, and converted speech (mean ± 95% confidence interval).
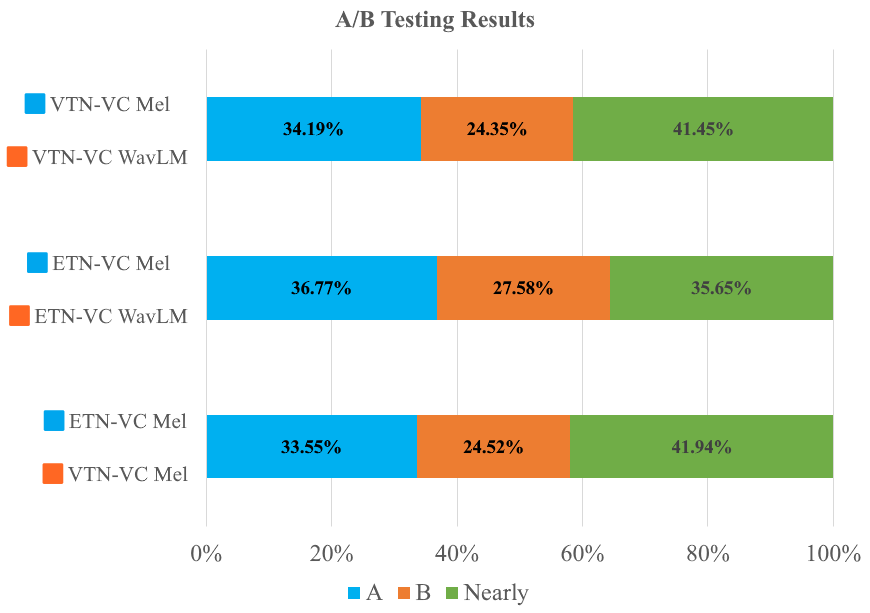
- Fig. 2. The intelligibility A/B test results for different model configurations. The bars represent the percentage of subjects’ votes for each system (system A, system B, and no preference)
Audio Sample
sample 1 (CEL using WavLM features and NEL using Mel-spectrograms, respectively.)
| Model | transcription: 他捐了很多衣物給災區 (Ta juan le hen duo yiwu gei zaiqu) |
|---|---|
| CEL speech | |
| NEL speech | |
| VTN-VC CEL | |
| VTN-VC NEL | |
| ETN-VC CEL | |
| ETN-VC NEL | |
| NL speech |
sample 2 (CEL using WavLM features and NEL using Mel-spectrograms, respectively.)
| Model | transcription: 電視報導那裡發生地震 (dian shi bao dao na li fa sheng di zhen) |
|---|---|
| CEL speech | |
| NEL speech | |
| VTN-VC CEL | |
| VTN-VC NEL | |
| ETN-VC CEL | |
| ETN-VC NEL | |
| NL speech |
sample 3 (CEL using WavLM features and NEL using Mel-spectrograms, respectively.)
| Model | transcription: 我把不用的傢俱送人了 (Wo ba bu yong de jia ju song ren le) |
|---|---|
| CEL speech | |
| NEL speech | |
| VTN-VC CEL | |
| VTN-VC NEL | |
| ETN-VC CEL | |
| ETN-VC NEL | |
| NL speech |
sample 4 (CEL using WavLM features and NEL using Mel-spectrograms, respectively.)
| Model | transcription: 昨天他向我借了三百塊 (Zuo tian ta xiang wo jie le san bai kuai) |
|---|---|
| CEL speech | |
| NEL speech | |
| VTN-VC CEL | |
| VTN-VC NEL | |
| ETN-VC CEL | |
| ETN-VC NEL | |
| NL speech |
Spectrogram
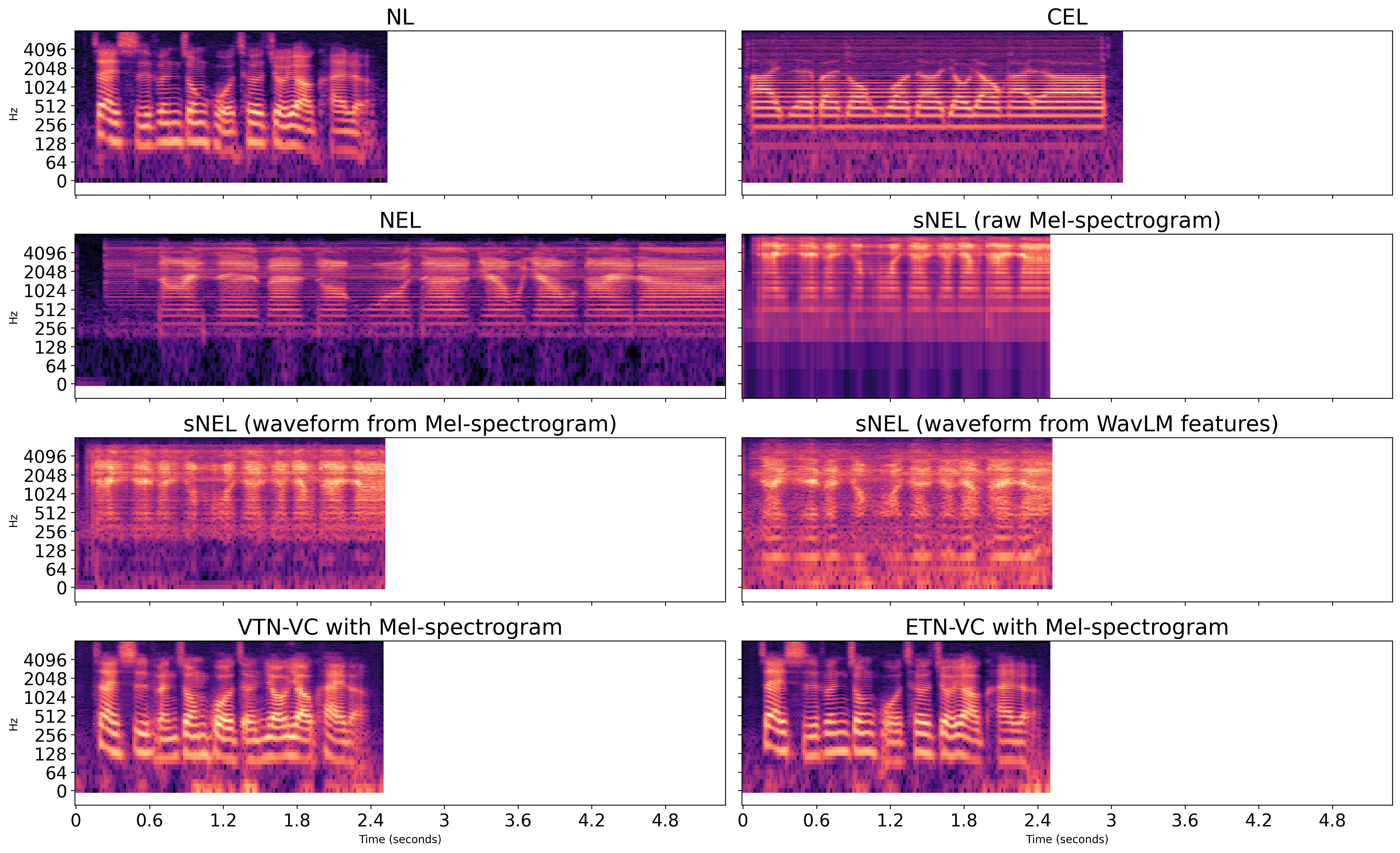
- Fig. 3. Mel-spectrograms of NL, CEL, and NEL speech, sNEL speech synthesized using Mel-spectrogram and WavLM features, and converted speech of VTN-VC and ETN-VC (both with Mel-spectrogram). NEL speech is typically longer, whereas synthesized and converted speech follow NL durations due to seq2seq alignment.